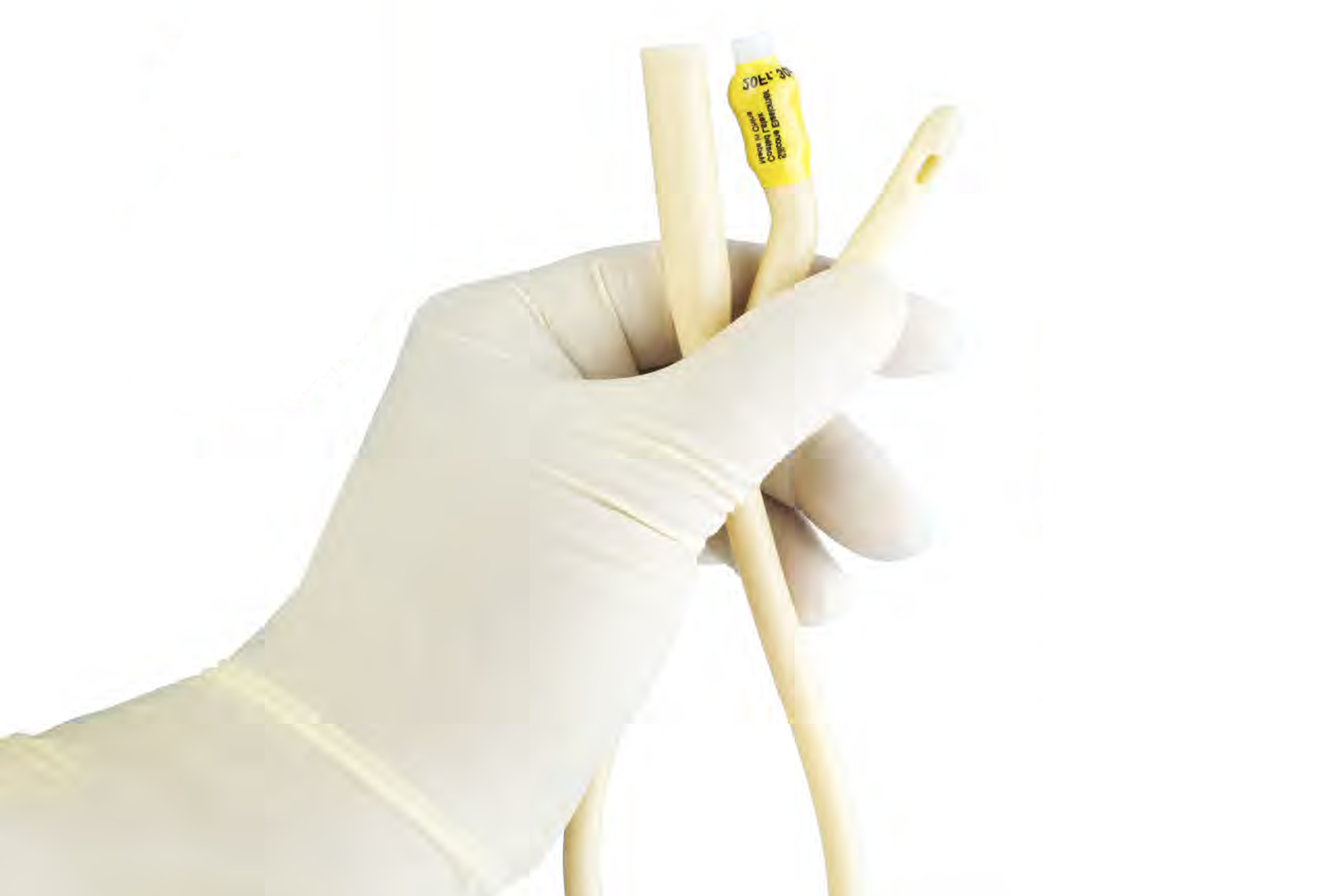
The method for coating urinary catheters with nanoparticles
Detail
Coating medical instruments to prevent and eliminate bacterial infections or biofilm formation can significantly reduce cross-infections among patients, especially those with open wounds, those requiring internal medical devices, or those with weakened immune systems. Currently, popular methods for coating medical instruments include dip-coating layer by layer with antibacterial drugs or agents to eliminate microbes and sterilize the equipment. However, these methods have the disadvantage of short-term antimicrobial effectiveness since the agents used cannot maintain their potency for long periods.
Spray coating is another common technique used to apply active substances onto medical instruments such as wound dressings and catheters to reduce bacterial infections. Researchers have developed a method for coating medical instruments by combining layer-by-layer dip-coating with nanoparticle spray coating that includes antibacterial components. This method effectively coats both the internal and external surfaces of medical instruments.
Nanoparticles in the form of micelles encapsulate antibacterial substances within them, while nanospheres store these substances within the interstitial spaces between multiple polymer molecular chains that are intertwined. These nanoparticles gradually release the antibacterial agents when the medical instruments come into contact with bodily fluids.
Technology readiness level
——-Transfer
——-Prototype
——-Experimental
——-Initial
Technology strengths
Creator
Assoc.Prof. Dr. Norased Nasongkla and colleagues
Coordinator: Technology Commercialization

